简介
Redis 是开源的、高性能的 key-value 数据库。Redis 与其他 key-value 缓存产品有以下三个特点:
- Redis支持数据的持久化,可以将内存中的数据保存在磁盘中,重启时可以再次加载进行使用。
- Redis不仅仅支持简单的 key-value 类型的数据,同时还提供 list(列表)、hash(哈希)、set(集合)、zset(有序集合) 数据结构的存储。
- Redis支持数据的备份,即 master-slave 模式的数据备份。
优势
- 性能极高:Redis速度非常快,读的速度是110000次/s,写的速度是81000/s。
- 支持丰富的数据类型:Redis支持 string、hash、list、set、zset 五种数据类型。
- 原子性:Redis的所有操作都是原子性的,这可确保在多个客户端同时访问时的线程安全问题(单线程),单个操作是原子性的,多个操作也支持事务(即原子性),通过MULTI和EXEC指令包起来。
- 丰富的特性:Redis可用于许多应用场景,如缓存(注意缓存的添加不能影响正常的业务逻辑)、消息队列(Redis本身支持发布/订阅)、应用程序中的任何短期数据(如Web应用程序会话)、网页命中数等。
数据存储类型
Redis支持 string、hash、list、set、zset 五种数据类型。
| Data Type | Java Data Type |
|---|---|
| string | Map<String, String> |
| hash | Map<String, Map<String, String>> |
| list | Map<String, List |
| set | Map<String, Set |
| zset | Map<String, SortedSet |
string
字符串类型是Redis中最为基础的数据存储类型,它在Redis中是二进制安全的,这便意味着该类型可以接受任何格式的数据,如JPEG图像数据或Json对象描述信息等,在Redis中字符串类型的value最多可以容纳的数据长度是512M。
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| SET key value | This command sets the value at the specified key. |
| GET key | Gets the value of a key. |
| GETRANGE key start end | Gets a substring of the string stored at a key. |
| GETSET key value | Sets the string value of a key and return its old value. |
| GETBIT key offset | Returns the bit value at the offset in the string value stored at the key. |
| MGET key1 [key2..] | Gets the values of all the given keys. |
| SETBIT key offset value | Sets or clears the bit at the offset in the string value stored at the key. |
| SETEX key seconds value | Sets the value with the expiry of a key. |
| SETNX key value | Sets the value of a key, only if the key does not exist. |
| SETRANGE key offset value | Overwrites the part of a string at the key starting at the specified offset. |
| STRLEN key | Gets the length of the value stored in a key. |
| MSET key value [key value …] | Sets multiple keys to multiple values. |
| MSETNX key value [key value …] | Sets multiple keys to multiple values, only if none of the keys exist. |
| PSETEX key milliseconds value | Sets the value and expiration in milliseconds of a key. |
| INCR key | Increments the integer value of a key by one. |
| INCRBY key increment | Increments the integer value of a key by the given amount. |
| INCRBYFLOAT key increment | Increments the float value of a key by the given amount. |
| DECR key | Decrements the integer value of a key by one. |
| DECRBY key decrement | Decrements the integer value of a key by the given number. |
| APPEND key value | Appends a value to a key. |
hash
Redis中的hash类型是具有string field和string value的map容器,所以它是表示对象的完美数据类型。在Redis中,每个hash可以存储多达40亿个字段值对。
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| HDEL key field2 [field2] | Deletes one or more hash fields. |
| HEXISTS key field | Determines whether a hash field exists or not. |
| HGET key field | Gets the value of a hash field stored at the specified key. |
| HGETALL key | Gets all the fields and values stored in a hash at the specified key. |
| HINCRBY key field increment | Increments the integer value of a hash field by the given number. |
| HINCRBYFLOAT key field increment | Increments the float value of a hash field by the given amount. |
| HKEYS key | Gets all the fields in a hash. |
| HLEN key | Gets the number of fields in a hash. |
| HMGET key field1 [field2] | Gets the values of all the given hash fields. |
| HMSET key field1 value1 [field2 value2 ] | Sets multiple hash fields to multiple values. |
| HSET key field value | Sets the string value of a hash field. |
| HSETNX key field value | Sets the value of a hash field, only if the field does not exist. |
| HVALS key | Gets all the values in a hash. |
| HSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] | Incrementally iterates hash fields and associated values. |
list
在Redis中,list类型是按照插入顺序排序的字符串链表,和数据结构中的普通链表一样,我们可以在其头部和尾部添加新的元素。List中可以包含的最大元素数量是4294967295(2^32-1)。
在插入时,如果该键并不存在,Redis将为该键创建一个新的链表。与此相反,如果链表中所有的元素均被移除,那么该键也将会被从数据库中删除。
从元素插入和删除的效率来看,如果我们是在链表的两头插入或删除元素,这将会是非常高效的操作,即使链表中已经存储了百万条记录,该操作也可以在常量时间内完成;然而需要说明的是,如果元素插入或删除操作是作用于链表中间,那将会是非常低效的(因为需要进行移动操作)。
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| BLPOP key1 [key2 ] timeout | Removes and gets the first element in a list, or blocks until one is available. |
| BRPOP key1 [key2 ] timeout | Removes and gets the last element in a list, or blocks until one is available. |
| BRPOPLPUSH source destination timeout | Pops a value from a list, pushes it to another list and returns it; or blocks until one is available. |
| LINDEX key index | Gets an element from a list by its index. |
| LINSERT key BEFORE(AFTER) pivot value | Inserts an element before or after another element in a list. |
| LLEN key | Gets the length of a list. |
| LPOP key | Removes and gets the first element in a list. |
| LPUSH key value1 [value2] | Prepends one or multiple values to a list. |
| LPUSHX key value | Prepends a value to a list, only if the list exists. |
| LRANGE key start stop | Gets a range of elements from a list. |
| LREM key count value | Removes elements from a list. |
| LSET key index value | Sets the value of an element in a list by its index. |
| LTRIM key start stop | Trims a list to the specified range. |
| RPOP key | Removes and gets the last element in a list. |
| RPOPLPUSH source destination | Removes the last element in a list, appends it to another list and returns it. |
| RPUSH key value1 [value2] | Appends one or multiple values to a list. |
| RPUSHX key value | Appends a value to a list, only if the list exists. |
set
在Redis中,set类型是没有排序的字符串集合。set可包含的最大元素数量是4294967295(2^32-1)。
和list类型一样,我们也可以在该类型的数据值上执行添加、删除或判断某一元素是否存在等操作。需要说明的是,这些操作的时间复杂度为O(1)(无论set集合中包含的元素数量是多少都是常量时间)。
和list类型不同的是,set集合中不允许出现重复的元素,换句话说,如果多次添加相同元素,set中将仅保留该元素的一份拷贝。
和list类型相比,set类型在功能上还存在着一个非常重要的特性,即在服务器端完成多个sets之间的聚合计算操作,如unions、intersections和differences操作,由于这些操作均在服务端完成,因此效率极高,并且也节省了大量的网络IO开销。
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| SADD key member1 [member2] | Adds one or more members to a set. |
| SCARD key | Gets the number of members in a set. |
| SDIFF key1 [key2] | Subtracts multiple sets. |
| SDIFFSTORE destination key1 [key2] | Subtracts multiple sets and stores the resulting set in a key. |
| SINTER key1 [key2] | Intersects multiple sets. |
| SINTERSTORE destination key1 [key2] | Intersects multiple sets and stores the resulting set in a key. |
| SISMEMBER key member | Determines if a given value is a member of a set. |
| SMEMBERS key | Gets all the members in a set. |
| SMOVE source destination member | Moves a member from one set to another. |
| SPOP key | Removes and returns a random member from a set. |
| SRANDMEMBER key [count] | Gets one or multiple random members from a set. |
| SREM key member1 [member2] | Removes one or more members from a set. |
| SUNION key1 [key2] | Adds multiple sets. |
| SUNIONSTORE destination key1 [key2] | Adds multiple sets and stores the resulting set in a key. |
| SSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] | Incrementally iterates set elements. |
zset
和set类型极为相似,它们都是字符串的集合,都不允许重复的成员出现在一个set中。它们之间的主要差别是zset中的每一个成员都会有一个分数(score)与之关联,Redis正是通过score来为集合中的成员进行从小到大的排序。然而需要说明的是,尽管zset中的成员必须是唯一的,但是score却是可以重复的。
在zset中,添加、删除或测试成员是否存在都是非常快速的操作,其时间复杂度为O(1)(无论set集合中包含的元素数量是多少都是常量时间)。
由于zset中的成员在集合中的位置是有序的,因此,即便是访问位于集合中部的成员也仍然是非常高效的。事实上,Redis所具有的这一特征在很多其它类型的数据库中是很难实现的,换句话说,在这点上要想达到和Redis同样的高效,在其它数据库中进行建模是非常困难的。
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ZADD key score1 member1 [score2 member2] | Adds one or more members to a sorted set, or updates its score, if it already exists. |
| ZCARD key | Gets the number of members in a sorted set. |
| ZCOUNT key min max | Counts the members in a sorted set with scores within the given values. |
| ZINCRBY key increment member | Increments the score of a member in a sorted set. |
| ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key [key …] | Intersects multiple sorted sets and stores the resulting sorted set in a new key. |
| ZLEXCOUNT key min max | Counts the number of members in a sorted set between a given lexicographical range. |
| ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] | Returns a range of members in a sorted set, by index. |
| ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count] | Returns a range of members in a sorted set, by lexicographical range. |
| ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT] | Returns a range of members in a sorted set, by score. |
| ZRANK key member | Determines the index of a member in a sorted set. |
| ZREM key member [member …] | Removes one or more members from a sorted set. |
| ZREMRANGEBYLEX key min max | Removes all members in a sorted set between the given lexicographical range. |
| ZREMRANGEBYRANK key start stop | Removes all members in a sorted set within the given indexes. |
| ZREMRANGEBYSCORE key min max | Removes all members in a sorted set within the given scores. |
| ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] | Returns a range of members in a sorted set, by index, with scores ordered from high to low. |
| ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES] | Returns a range of members in a sorted set, by score, with scores ordered from high to low. |
| ZREVRANK key member | Determines the index of a member in a sorted set, with scores ordered from high to low. |
| ZSCORE key member | Gets the score associated with the given member in a sorted set. |
| ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key …] | Adds multiple sorted sets and stores the resulting sorted set in a new key. |
| ZSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] | Incrementally iterates sorted sets elements and associated scores. |
key操作
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| DEL key | This command deletes the key, if it exists. |
| DUMP key | This command returns a serialized version of the value stored at the specified key. |
| EXISTS key | This command checks whether the key exists or not. |
| EXPIRE key seconds | Sets the expiry of the key after the specified time. |
| EXPIREAT key timestamp | Sets the expiry of the key after the specified time. Here time is in Unix timestamp format. |
| PEXPIRE key milliseconds | Set the expiry of key in milliseconds. |
| PEXPIREAT key milliseconds-timestamp | Sets the expiry of the key in Unix timestamp specified as milliseconds. |
| KEYS pattern | Finds all keys matching the specified pattern. |
| MOVE key db | Moves a key to another database. |
| PERSIST key | Removes the expiration from the key. |
| PTTL key | Gets the remaining time in keys expiry in milliseconds. |
| TTL key | Gets the remaining time in keys expiry. |
| RANDOMKEY | Returns a random key from Redis. |
| RENAME key newkey | Changes the key name. |
| RENAMENX key newkey | Renames the key, if a new key doesn’t exist. |
| TYPE key | Returns the data type of the value stored in the key. |
事务
在事务中的所有命令都将会被串行化顺序执行,事务执行期间,Redis不会再为其它客户端的请求提供任何服务,从而保证了事务的原子性。
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| DISCARD | Discards all commands issued after MULTI. |
| EXEC | Executes all commands issued after MULTI. |
| MULTI | Marks the start of a transaction block. |
| UNWATCH | Forgets about all watched keys. |
| WATCH key [key …] | Watches the given keys to determine the execution of the MULTI/EXEC block. |
脚本
从Redis 2.6版本开始通过内嵌支持 Lua 环境,用于执行脚本的常用命令是EVAL。
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| EVAL script numkeys key [key …] arg [arg …] | Executes a Lua script. |
| EVALSHA sha1 numkeys key [key …] arg [arg …] | Executes a Lua script. |
| SCRIPT EXISTS script [script …] | Checks the existence of scripts in the script cache. |
| SCRIPT FLUSH | Removes all the scripts from the script cache. |
| SCRIPT KILL | Kills the script currently in execution. |
| SCRIPT LOAD script | Loads the specified Lua script into the script cache. |
持久化
- 无持久化:我们可以通过配置的方式禁用Redis的持久化功能,这样我们就可以将Redis视为一个功能加强版的memcached了。
- RDB(Relational Data Base)持久化:该机制是指在指定的时间间隔内将内存中的数据集快照写入磁盘。
- AOF(Append Only File)持久化:该机制将以日志的形式记录服务器所处理的每一个写操作,在Redis服务器启动之初会读取该文件来重新构建数据库,以保证启动后数据库中的数据是完整的。
- 同时应用AOF和RDB:AOF和RDB两种持久化方式是可以同时存在的,但是当Redis重启时,AOF文件会被优先用于重建数据。
集群
Redis提供了几种集群的方式:主从(Master-Slave)复制、哨兵(Sentinel)机制、Redis-Cluster集群模式
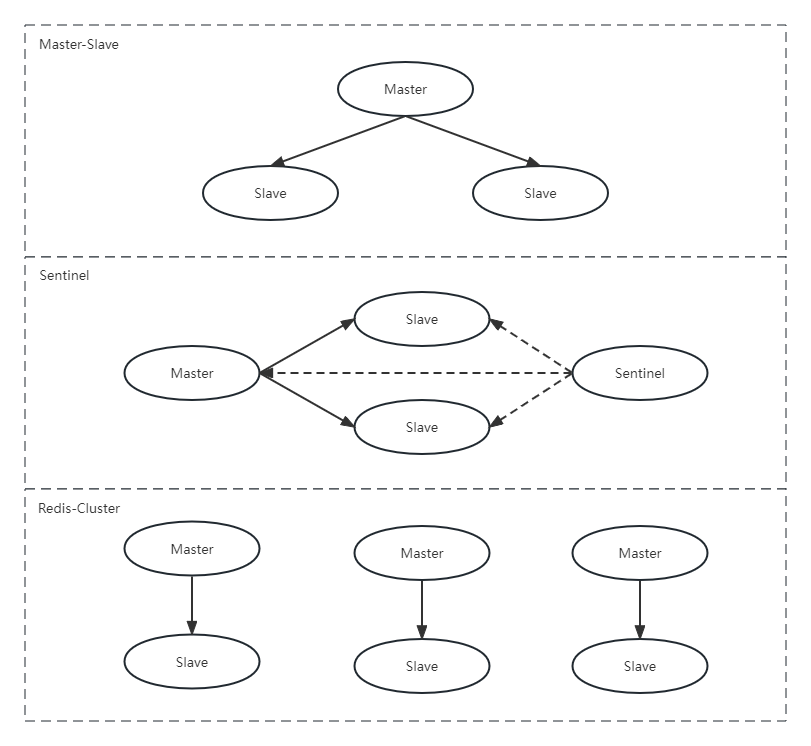
主从复制
工作机制
当Slave启动后,主动向Master发送SYNC命令。Master接收到SYNC命令后在后台保存快照(RDB持久化)和缓存保存快照这段时间的命令,然后将保存的快照文件和缓存的命令发送给Slave。Slave接收到快照文件和命令后加载快照文件和缓存的执行命令。
复制初始化后,Master每次接收到的写命令都会同步发送给Slave,保证主从数据一致性。
特点
- Master可以进行读写操作,当读写操作导致数据变化时会自动将数据同步给Slave
- Slave一般都是只读的,并且接收Master同步过来的数据
- 一个Master可以拥有多个Slave,但是一个Slave只能对应一个Master
1 | #bind 127.0.0.1 |
哨兵机制
Redis主从复制的缺点:没有办法对 Master 进行动态选举,需要使用 Sentinel 机制完成动态选举。
特点
- 监控Master和Slave是否正常运行
- Master出现故障时,自动将Slave转化为Master
- 多哨兵配置的时候,哨兵之间也会自动监控
- 多个哨兵可以监控同一个redis
无论是主从模式还是哨兵模式,这两个模式都有一个问题,不能水平扩容,并且这两个模式的高可用特性都会受到Master主节点内存的限制。
Cluster集群模式
Redis 的哨兵模式基本已经可以实现高可用,读写分离 ,但是在这种模式下每台 Redis 服务器都存储相同的数据,很浪费内存,所以在 redis3.0上加入了 Cluster 集群模式,Redis Cluster是一种服务器 Sharding 技术,实现了 Redis 的分布式存储,也就是说每台 Redis 节点上存储不同的内容。
- Redis集群的键空间被分割为16384个槽(slot),集群的最大节点数量也是16384个。
- Redis集群把所有的物理节点映射到[0-16383]槽上,Cluster负责维护 node <-> slot <-> value。
- Redis集群中内置了16384个哈希槽,当需要在Redis集群中放置一个 key-value 时,Redis通过 CRC16(key) mod 16384 算法将键映射到指定的槽上。
哈希槽机制一个很明显的优势就是在处理并发的场景,因为它将数据集进行了分割,实际上减小了锁的粒度,从而扩大了并发度。Java中的ConcurrentHashMap容器就是应用这种机制来实现并发的典型例子。
搭建
- 修改配置文件 redis.conf 中的端口号并将cluster-enabled设置为yes来启用集群
- 启动所有redis实例
- 将ruby脚本 redis-trib.rb 拷贝到redis-cluster目录下
- 执行ruby脚本创建集群
1 | ./redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 127.0.0.1:7001 127.0.0.1:7002 127.0.0.1:7003 127.0.0.1:7004 127.0.0.1:7005 127.0.0.1:7006 |
容错
- 节点检测(投票机制)
每一个节点都存有这个集群所有主节点以及从节点的信息,它们之间通过互相的PING-PONG判断是否节点可以连接上,如果有一半以上的节点去PING一个节点的时候没有回应,集群就认为这个节点宕机了,然后去连接它的备用节点(集群中一个节点的Master挂掉,从节点会提升为主节点)。 - 集群进入fail状态的必要条件
- 如果集群任意Master挂掉且当前Master没有Slave,集群进入fail状态(即集群的slot映射[0-16383]不完成时进入fail状态)。
- 如果集群有超过半数以上Master挂掉,无论是否有Slave,集群进入fail状态。
使用Redis需要注意的问题
缓存使用原则
缓存的添加不应该影响原有业务。
缓存更新
如果先让缓存失效再更新数据库,可能在让缓存失效后的瞬间,其他线程刚好去访问缓存,这时发现数据不存在就会去查询DB(脏数据)后再回设到缓存中,这样就会导致脏数据的出现。
解决方案:先更新数据库,再让缓存失效。当然,在更新完数据库,未来得及让缓存失效的瞬间,其他线程访问到的缓存中的数据依然是脏数据,不过概率相对较小。
缓存击穿/缓存穿透
一般的缓存系统,都是按照key去缓存查询,如果不存在对应的value就会去DB查找。如果key对应的value是一定不存在的,并且对该key并发请求量很大,就会对DB造成很大的压力,这就叫做缓存穿透。
解决方案:业界比较常用的做法是使用使用互斥锁(mutex)。简单地来说,就是在缓存失效的时候(判断拿出来的值为空),不是立即去load db而是先使用缓存工具的某些带成功操作返回值的操作(比如Redis的SETNX或者Memcache的ADD)去set一个mutex key,当操作返回成功时,再进行load db的操作并回设缓存,否则,就重试整个get缓存的方法。
1 | public String get(key) { |
缓存雪崩
缓存雪崩是指在我们设置缓存时采用了相同的过期时间,导致缓存在某一时刻同时失效,请求全部转发到DB,DB瞬时压力过重雪崩。
解决方案:将缓存失效时间分散开,比如我们可以在原有的失效时间基础上增加一个随机值。
常见问题
为什么Redis是单线程的?
因为Redis是基于内存的操作,CPU不是Redis的瓶颈,Redis的瓶颈最有可能是机器内存的大小或者网络带宽。既然单线程容易实现,而且CPU不会成为瓶颈,那就顺理成章地采用单线程的方案了(单线程下已经很快了,没有必要再使用多线程了,并且使用单线程还省去了多线程之间的上下文切换导致的开销);但是,使用单线程的方式就无法发挥多核CPU性能,不过我们可以通过在单机开多个Redis实例来完善。
单线程的Redis为什么快?
Redis使用的是非阻塞IO,IO多路复用技术,使用了单线程来轮询事件,将IO的读、写、连接都转换成了事件,这样使得只有在连接真正有读写事件发生时,才会调用函数来进行读写,就大大地减少了系统开销,并且不必为每个连接都创建一个线程,不用去维护多个线程,还避免了多线程之间的上下文切换导致的开销。
